Lancom 1721 VPN Manual
Læs gratis den danske manual til Lancom 1721 VPN (76 sider) i kategorien Router. Denne vejledning er vurderet som hjælpsom af 27 personer og har en gennemsnitlig bedømmelse på 4.8 stjerner ud af 14 anmeldelser.
Har du et spørgsmål om Lancom 1721 VPN, eller vil du spørge andre brugere om produktet?
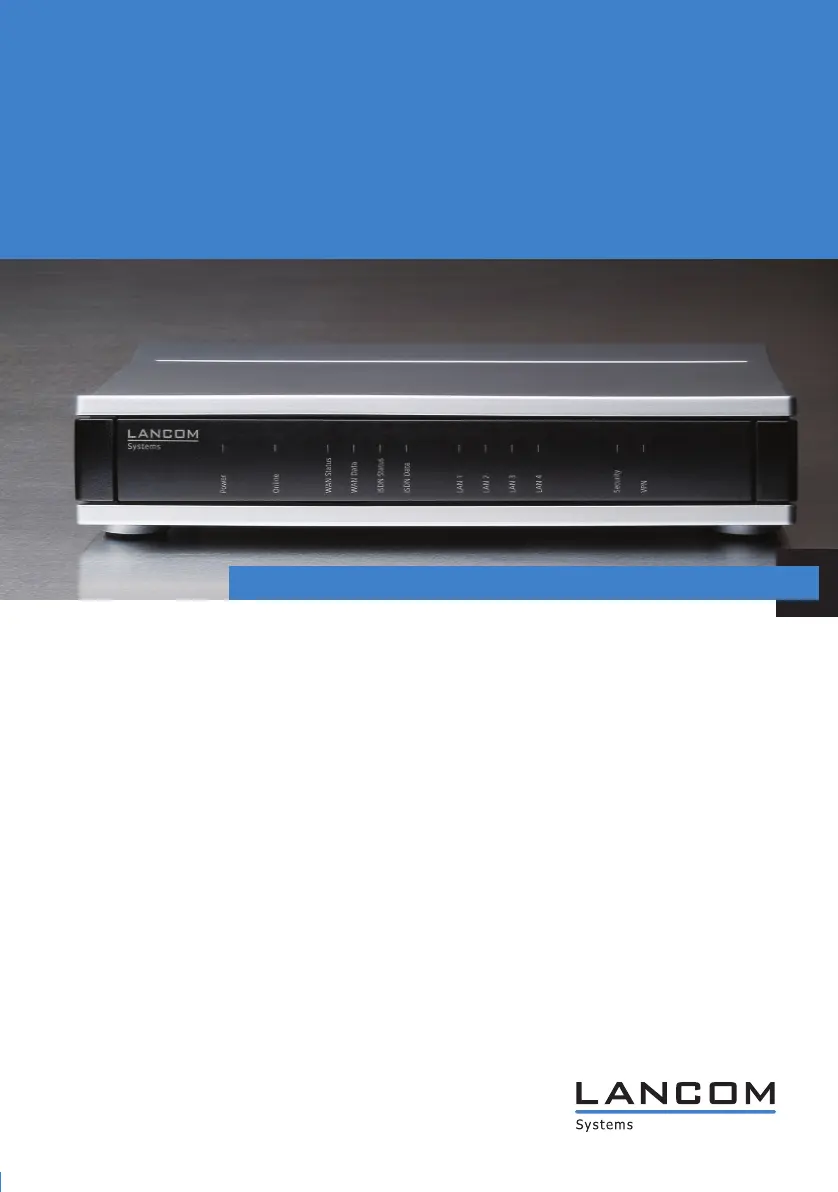

Produkt Specifikationer
| Mærke: | Lancom |
| Kategori: | Router |
| Model: | 1721 VPN |
| Relativ luftfugtighed ved drift (H-H): | 0 - 80 % |
| Ethernet LAN-porte (RJ-45): | 5 |
| Driftstemperatur (T-T): | 5 - 40 °C |
| Dimensioner (BxDxH): | 210 x 140 x 45 mm |
| Forbindelsesteknologi: | Ledningsført |
| Certificering: | CE, EN 60950, EN55022, EN55024 |
| Understøttede netværksprotokoller: | TCP/IP, IPX/SPX, PPTP, UDP/IP, NetBEUI/NetBIOS, NTP, VoIP, ICMP/IP, IP/IPX, IPSec, PPPoE, PPPoA, IPoA |
| Effektkrav: | 230 V |
| Antal USB-porte: | 1 |
| Maksimal dataoverførselshastighed: | 0.1 Gbit/sek. |
| Antal kanaler: | 5 kanaler |
| Antal RJ-11-porte: | 1 |
| ADSL: | Ja |
| Administrationsprotokoller: | SNMP 2, SNMP, Telnet, HTTP, HTTPS |
| Understøttede protokoller: | ITU X.75, HDLC, ITU G.992.5, ITU G.992.1 (G.DMT) An. A |
| Understøtter ISDN-forbindelse: | Ja |
| Datalink-protokol: | Ethernet, Fast Ethernet, PPP |
| Routing-protokoller: | RIP-1, RIP-2 |
| Godkendelsesmetode: | RADIUS, SSH |
| Udvekslingsprotokoller: | Ethernet |
| Protokol for digitalt signal: | EURO-ISDN, ISDN 1TR6, ADSL, ISDN DSS1/ETSI, ADSL o ISDN, ADSL2+ |
Har du brug for hjælp?
Hvis du har brug for hjælp til Lancom 1721 VPN stil et spørgsmål nedenfor, og andre brugere vil svare dig
Router Lancom Manualer








Router Manualer
- Conceptronic
- Media-Tech
- AVMATRIX
- TRENDnet
- Sitecom
- Analog Way
- Metabo
- Huawei
- Gembird
- I-Tec
- Roland
- Kraun
- Dovado
- Digitalinx
- Yato
Nyeste Router Manualer









